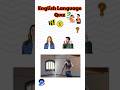
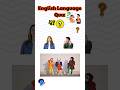
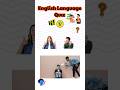
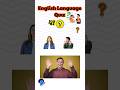
Read about the Evans sisters. Correct the information in the sentences below. Use the information in the text.
This is a reading and listening activity. Students read, listen, and answer the questions. The activity has an answer key.
*Download this worksheet: Simple present tense reading, listening and grammar worksheet.
Simple Present Tense: Explained for Elementary Students
1. Understanding the Simple Present Tense
- Definition: The simple present tense is used to talk about habitual actions, general truths, and routines. It’s used for actions that happen regularly, facts, and things that are always true.
- Examples of Usage:
- “I play soccer every Saturday.”
- “The sun rises in the east.”
- “She loves chocolate.”
2. Forming the Simple Present Tense
- Affirmative Sentences: In affirmative sentences, we use the base form of the verb (infinitive without “to”) for all subjects except “he,” “she,” and “it,” where we add “s” or “es” to the verb.
- Examples:
- “I play tennis.” (Base form of the verb “play”)
- “He plays tennis.” (Adding “s” for the third person singular)
- Examples:
- Negative Sentences: In negative sentences, we use the auxiliary verb “do” (or “does” for third person singular) + “not” before the base form of the verb.
- Examples:
- “I do not play tennis.” (Adding “do not” before the base form “play”)
- “She does not play tennis.” (Using “does not” before the base form “play”)
- Examples:
- Questions: In questions, we use the auxiliary verb “do” (or “does” for third person singular) + the base form of the verb.
- Examples:
- “Do you play tennis?” (Using “do” before the base form “play”)
- “Does she play tennis?” (Using “does” before the base form “play”)
- Examples:
Simple Present Tense Usage Table with Pronouns and Answers:
| Subject Pronoun | Affirmative Sentence | Negative Sentence | Question Sentence | Answer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | I play soccer. | I do not play soccer. / I don’t play soccer. | Do I play soccer? | Yes, I play soccer. |
| You | You play soccer. | You do not play soccer. / You don’t play soccer. | Do you play soccer? | Yes, you play soccer. |
| He | He plays soccer. | He does not play soccer. / He doesn’t play soccer. | Does he play soccer? | Yes, he plays soccer. |
| She | She plays soccer. | She does not play soccer. / She doesn’t play soccer. | Does she play soccer? | Yes, she plays soccer. |
| It | The dog plays soccer. | The dog does not play soccer. / The dog doesn’t play soccer. | Does the dog play soccer? | Yes, the dog plays soccer. |
| We | We play soccer. | We do not play soccer. / We don’t play soccer. | Do we play soccer? | Yes, we play soccer. |
| They | They play soccer. | They do not play soccer. / They don’t play soccer. | Do they play soccer? | Yes, they play soccer. |
Note:
- In affirmative sentences, the base form of the verb is used for all pronouns except “he,” “she,” and “it,” where we add “s” or “es” to the verb.
- In negative sentences, “do” (or “does” for third person singular) + “not” is used before the base form of the verb.
- In question sentences, “do” (or “does” for third person singular) is used before the base form of the verb.
3. State Verbs in the Simple Present Tense
- Definition: State verbs express states, conditions, or situations rather than actions. They are not typically used in continuous (progressive) forms and are often used in the simple present tense.
- Examples of State Verbs:
- Emotions and Feelings:
- love, like, hate, dislike, adore, detest, prefer, appreciate
- admire, envy, fear, loathe, cherish, enjoy, appreciate
- Senses:
- see, hear, smell, taste, feel (in the sense of experiencing a sensation)
- Mental States and Perception:
- think, believe, know, understand, remember, forget, realize
- recognize, doubt, suppose, expect, mean, perceive, doubt
- Physical States and Appearances:
- be, seem, appear, look (in the sense of appearance), sound (in the sense of appearance)
- resemble, have (in the sense of possession), belong, own, contain
- Possession and Relationships:
- have (in the sense of possession), possess, belong (in the sense of ownership), own, contain
- need, require, deserve, owe, consist (in the sense of composition)
- Emotions and Feelings:
State Verbs in the Simple Present Tense
- State verbs describe a condition or state, so they often remain the same in both affirmative and negative sentences.
- Example:
- “She likes ice cream.” (Affirmative)
- “She does not like ice cream.” (Negative)