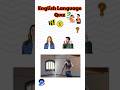
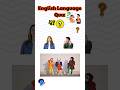
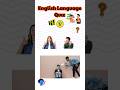
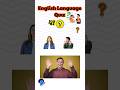
Read and listen to the two texts. Are sentences 1-8 ‘Right’ (A) or ‘Wrong’ (B)?
Circle the correct words.
This ESL EFL free worksheet contains exercises about family members. Learners can also practice and spot: Simple present tense, plurals, have/has, the verb to be,
adverbs of frequency, love/like+v-ing, and, but and possessive adjectives from the text. The worksheet has an answer key.
1. The Simple Present Tense:
Definition:
The simple present tense is used to describe actions that are habitual, routine, or generally true. It is formed by using the base form of the verb.
Examples:
| Pronoun | Positive Statement | Negative Statement | Question |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I play tennis every weekend. | I don’t play tennis every weekend. | Do I play tennis every weekend? |
| You | You like chocolate ice cream. | You don’t like chocolate ice cream. | Do you like chocolate ice cream? |
| He/She/It | She works at a bank. | She doesn’t work at a bank. | Does she work at a bank? |
| We | We study English together. | We don’t study English together. | Do we study English together? |
| They | They live in New York City. | They don’t live in New York City. | Do they live in New York City? |
Usage:
- Habitual Actions:
- Use the simple present tense to describe actions that happen regularly or habitually.
- Example: “I brush my teeth twice a day.”
- Use the simple present tense to describe actions that happen regularly or habitually.
- Facts and General Truths:
- Use the simple present tense to state facts or general truths.
- Example: “Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.”
- Use the simple present tense to state facts or general truths.
- Scheduled Events:
- Use the simple present tense to talk about scheduled future events, especially for timetables and schedules.
- Example: “The train departs at 9:00 AM tomorrow.”
- Use the simple present tense to talk about scheduled future events, especially for timetables and schedules.
- State Verbs:
- Use the simple present tense with state verbs to describe ongoing states or conditions.
- Example: “She loves chocolate.”
- Use the simple present tense with state verbs to describe ongoing states or conditions.
2. Adverbs of Frequency:
Definition:
Adverbs of frequency are words that describe how often something happens. They include words like always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, and never.
Examples:
| Adverb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Always | She always wakes up early in the morning. |
| Usually | I usually eat breakfast before work. |
| Often | They often go jogging in the park. |
| Sometimes | He sometimes forgets to bring his umbrella. |
| Rarely | We rarely eat out at fancy restaurants. |
| Never | She never misses her morning yoga routine. |
Usage:
- Place adverbs of frequency before the main verb in a sentence.
- Use them to describe how often an action occurs.
3. Plurals:
Definition:
Plurals are forms of words that refer to more than one person, thing, or entity. They are typically formed by adding -s or -es to the singular form of a noun.
Examples:
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Cat | Cats |
| Dog | Dogs |
| Car | Cars |
| Book | Books |
| Dish | Dishes |
| Potato | Potatoes |
Usage:
- Add -s to most nouns to form the plural.
- Add -es to nouns ending in -s, -x, -z, -ch, or -sh to form the plural.
- Some irregular nouns have unique plural forms.
4. Love/Like + V-ing:
Definition:
The construction “love/like + V-ing” is used to express enjoyment or preference for an activity or experience.
Examples:
- I love watching movies on weekends.
- She likes going for walks in the park.
- They love playing video games together.
Usage:
- Use “love/like + V-ing” to express enjoyment or preference for activities or experiences.
- The gerund form (-ing) of the verb follows “love” or “like” in this construction.