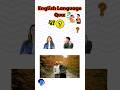
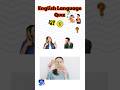
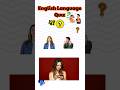
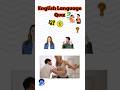
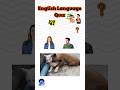
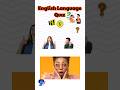
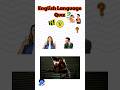
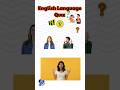
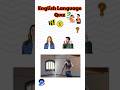
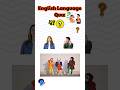
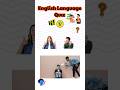
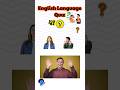
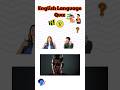
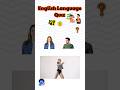
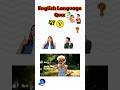
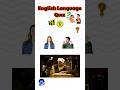
Read and listen about Tim and Bella.
Write short answers to the questions.
Some of the questions are about yesterday.
Write three things you could do when
you were three.
Write three things you can do now
that you couldn’t do when you were
three.
Write two things you couldn’t do when
you were three and you still can’t do!
This worksheet contains a reading and listening comprehension activity. It has questions and short Answers in the past tense. Students read, listen and answer. The answer key is attached.
The Simple Past Tense
The simple past tense is a fundamental aspect of English grammar. It allows us to discuss actions or events that occurred and concluded in the past. Here are the key points:
- Formation of Regular Verbs:
- For most regular verbs, we add -ed to the base form to create the past tense.
- Examples:
- She visited Paris last summer.
- He played the piano beautifully.
- Irregular Verbs:
- Irregular verbs have unique past forms that do not follow the regular -ed pattern.
- Examples:
- She ate sushi for dinner.
- They went to Spain for their holidays.
- Use of the Simple Past Tense:
- We use the simple past tense to talk about:
- Single Past Actions: Events that happened once in the past.
- I met my wife in 1983.
- They got home very late last night.
- Repeated Past Actions: Actions that occurred several times in the past.
- When I was a boy, I walked a mile to school every day.
- We swam a lot while we were on holiday.
- Past States or Habits: Situations that were true for some time in the past.
- I lived abroad for ten years.
- She played a lot of tennis when she was younger.
- Single Past Actions: Events that happened once in the past.
- We use the simple past tense to talk about:
- Questions in the Simple Past:
- To form questions, use did + the base form of the verb.
- Examples:
- Did you visit the museum yesterday?
- Where did they go on vacation?
- Negatives in the Simple Past:
- Use didn’t (did not) + the base form of the verb.
- Examples:
- They didn’t go to Spain this year.
- I didn’t see you yesterday.
“Could” and “Couldn’t”
- “Could”:
- Expresses possibility or ability in the past.
- Examples:
- I could swim when I was four.
- He could walk when he was two.
- Use the infinitive without “to” after “could”.
- “Couldn’t”:
- Indicates inability or lack of possibility in the past.
- Examples:
- She couldn’t ride a bike when she was three.
- My mum couldn’t swim when she was a child.
- Also use the infinitive without “to” after “couldn’t”.
- Questions with “Could”:
- Change the order of “could” and the person.
- Example:
- Could you play chess last year?
- Yes, I could.
- Hypotheses and Imaginary Situations:
- We can use the simple past tense to refer to the present or future in hypotheses (when imagining something).
Remember, mastering the simple past tense and modal verbs like “could” and “couldn’t” enhances your language proficiency. Practice using them to communicate effectively! ????
What should our team prepare for you?
What topics do you need?
“Thank you for taking the time to explore this topic with us! We hope you found the information helpful and insightful. Have any thoughts, questions, or additional examples to share? We’d love to hear from you in the comments below!
Don’t forget to spread the word by sharing this blog with your friends, family, and colleagues. Together, let’s continue to learn, grow, and connect with the world around us. Happy reading and sharing!”